What is a Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy?
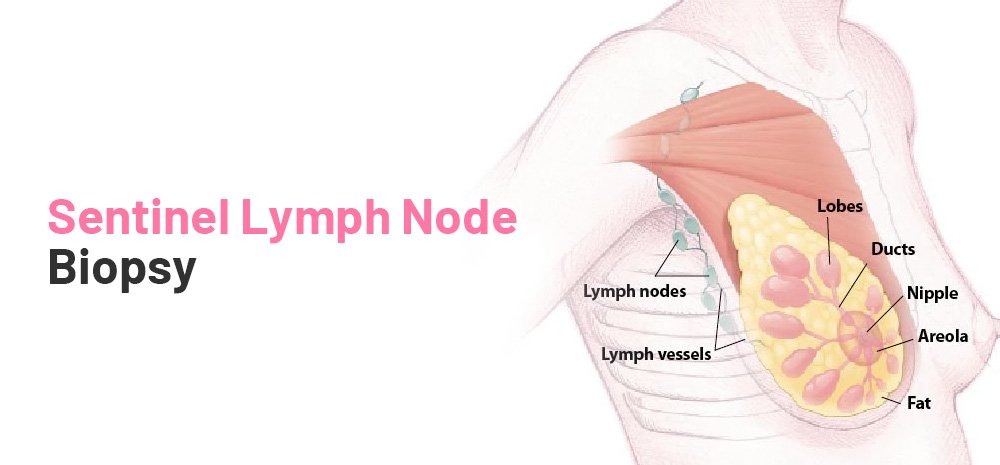
A sentinel node biopsy is a type of surgery that checks to see if cancer has spread from a primary tumour to the lymphatic system. It is most often used to check for breast cancer and melanoma.
The first few lymph nodes that a tumour drains into are the sentinel nodes. For a sentinel node biopsy, a tracer material is injected. This helps the surgeon find the sentinel nodes while they are operating. The sentinel nodes are taken out and looked at in a lab.
If cancer hasn’t spread and the sentinel lymph nodes are clear, there’s no need to take out any more lymph nodes. If the SLNB comes back negative, that means cancer hasn’t progressed to any of the lymph nodes or other organs in the area.
If the sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) comes back positive, it means that cancer has progressed to the lymph nodes in the immediate area (these are called regional lymph nodes) and perhaps beyond. Cancer’s stage (how far it has spread throughout the body) and treatment options can be narrowed down with this data.
If a sentinel lymph node biopsy shows that you have cancer, your doctor may suggest that more lymph nodes be taken out.
What is a lymph node?
The lymphatic system is made up of small, round organs called lymph nodes. The immune system includes the lymphatic system. It is made up of a network of blood vessels and organs that carry lymph, a clear fluid that carries white blood cells that fight infections, and fluid and waste from the cells and tissues of the body. Lymph can also carry cancer cells that have broken off from the main tumor in a person with cancer.
What is a sentinel lymph node?
A sentinel lymph node is the first lymph node cancer cells from a primary tumor are most likely to spread to. There isn’t always just one sentinel lymph node.
What takes place during a biopsy of a sentinel lymph node?
A radiotracer is a type of marker that is injected around the tumour by a doctor. The radiotracer moves through the lymphatic system, which is a path or network of lymph channels and nodes. This lets the surgeon see which lymph nodes drain the tumor first and find a sentinel lymph node.
Then, the doctor makes a small cut in the skin and looks for the lymph node that must be removed. A pathologist looks at the lymph node to see if it has cancer.
Why is a sentinel lymph node biopsy a good idea?
This method involves making a smaller cut and can keep people from needing more invasive surgery. It can cut down on the time it takes to get better after surgery and lower the risk of side effects like lymphedema, which is swelling that happens when more lymph nodes are taken out.
A sentinel lymph node biopsy is usually an outpatient procedure. This means that the patient can leave the hospital the same day unless they need more surgery.
What are the risks of taking a sample from a sentinel lymph node?
The risks are very low, but there is a very small chance, between 2% and 4%, that a sentinel lymph node might not be found.
Some patients worry about the radiotracer that is used to find the sentinel lymph node. Even though the tracer is radioactive, the particle it sends out has very low energy. There have been no reports of serious side effects; the only bad thing is that sometimes the injection hurts for a short time.
Patients with a sentinel lymph node biopsy may also get lymphedema, but it’s less likely than those with open surgery.
Can all types of cancer be staged with the help of SLNB?
No. Most of the time, SLNB is used to help figure out the stage of breast cancer and melanoma. It is sometimes used to determine how far along endometrial and penile cancers are (2). But it is being studied with other types of cancer, such as vulvar and cervical cancer (3), colorectal, gastric, esophageal, head and neck, thyroid, and non-small cell lung cancer (4).
Dr Mansi is the go-to guy for breast cancer procedures.
Having practised surgical oncology for over 12 years, Dr Mansi Chowhan has earned a stellar reputation in her speciality. Her specialities as an oncoplastic breast surgeon, head and neck surgeon, and plastic surgeon make her an exceptional medical professional.
Dr Mansi has been practising medicine for over a decade, and she has served as a physician at prestigious institutions like Fortis Healthcare (both in Delhi and Gurgaon), Artemis Hospital (also in Gurgaon), Paras Hospital (also in Gurgaon), and the Asian Institute of Medical Sciences (AIMS) (Faridabad).
More Expertise
EXCELLENT






